India Has Violated Its Obligations To UN On Peasant Rights
When the offices of the UN Secretary General, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, and the UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights to Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association supported the Indian peasants’ right of peaceful protest and assembly, they were reminding the Indian government of its general human rights obligations under the UN treaties that India has ratified and voluntarily undertaken to enforce at the national level.
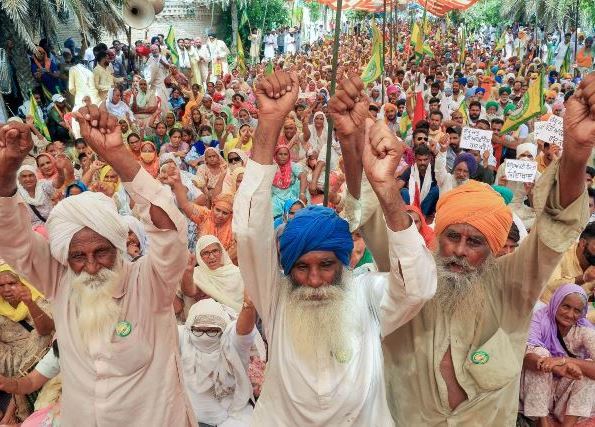
These top UN diplomats were cognisant of India’s response to the largely peaceful and unprecedented peasant protests in the form of disproportionate and impermissible law and order measures. Such measures are tantamount to criminalising the current peasant protests and are prohibited by the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Peasants and Other People Working in Rural Areas (the UNDROP).
It took more than seventeen years of campaign by the La Via Campesina, a global network campaign of peasants and rural workers organisations, to reach the milestone of the UNDROP’s adoption by the UN General Assembly on December 17, 2018. At this time, the Indian government has committed to follow the UNDROP which it not only voted for but actually proactively co-sponsored and campaigned for at the UN General Assembly.
The UNDROP brought peasant rights within the ambit of human rights and aimed to strengthen intergovernmental coordination and transnational agrarian solidarity. It is the first ever international law instrument that grants human rights to the majority rural population of global society and provides guidance to the governments on guaranteeing these rights. The UNDROP provides a framework for countries and the international community to strengthen the protection of the human rights of peasants and other rural people and to improve their living conditions.
The UNDROP’s fundamental premise is that the peasant and rural workers constitute 80% of the world’s population and are often victims of human rights violations and suffer from poverty. Peasant and rural landless workers, especially women, do not have equal control over land and other natural resources, or access to education and justice. It recognises the dignity of the world’s rural populations, their contributions to global food production, and their ‘special relationship’ to the land, water and nature, as well as their vulnerabilities to evictions, hazardous working conditions and political repression.
The UNDROP is a blueprint for potential national legislation dealing with the rights of peasants and rural workers. Although currently it is technically non-binding in a strict sense, it uses the term “shall” implying legal obligations of the countries and is an honour code that all UN members have agreed to uphold and incorporate in their national policy framework. Until it becomes a treaty with its own independent enforcement mechanism, the UN has deferred the UNDROP’s monitoring and instead asked all countries including India to include the UNDROP implementation measures in their periodic reports to the other UN human rights mechanisms.
ALSO READ: Are The Farm Laws Legal?
Importantly, the UNDROP prohibits criminalisation of peasants and rural workers protests and calls upon all countries including India to ensure that it shall not subject them to arbitrary arrest, detention, torture or other cruel, inhuman and degrading treatments when they exercise their right to freedom of expression and assembly. It also recognises the peasants and rural workers’ right to life, security of persons, freedom of movement, thought, opinion and expression, as well as association.
Despite India’s commitment at the UN not to criminalise any peasant struggle, the government introduced drastic measures in response to current protests such as interrupting access to water and electricity, limiting access to protest sites, barricading and fortifying protest sites, deploying paramilitary forces, disrupting internet services, registering criminal cases, arbitrarily detaining, torturing, and inflicting custodial and sexual violence against the protest leaders, protesters, supporters, and journalists.
From the beginning, the government acquiesced to the ruling party’s political propaganda apparatus that has engaged in a systematic vilification and dehumanisation campaign about the protests. It failed to publicly condemn all off and online attacks, and the use of hateful and misogynistic language against those connected with the protest.
The UNDROP requires India to ensure the primacy of peasants’ rights specified in the UNDROP over all international agreements, including those regulating trade, investments and intellectual property rights. For that purpose, it further mandates India to take legislative, administrative measures with full consultation of its rural populations. The government in drafting three farm laws has not made good faith efforts to facilitate the peasants’ right to actively participate in the legislative process.
The UNDROP states that India is obliged to take measures to favour peasants selling their products in markets and allow their families to attain an adequate standard of living. The measures enshrined in the three farm laws including the government’s unwillingness to give statutory power to the Minimum Support Price (MSP), adversely affecting the peasants fair access to the market and adequate standard of living, thereby breaching its commitment to the UNDROP.
Without any philosophical or ideological shift at government level or its explicit reservation to the implementation of the UNDROP, India’s volte face reveals its apparent intent to not comply with the UNDROP’s key provisions. The Indian governmental leadership understands the gravity of the situation about the agrarian crisis and protests, and understands its obligations to the peasants, yet it is making a strategic decision that dispute resolution and conflict prevention efforts are not worth the political costs.
A very simple understanding of the holistic configuration of the current protest dynamics indicates various imminent warning signs for the protests spiraling into a larger unmanageable crisis, with devastating consequences for peasants, rural workers, police and armed forces, their families, and the whole social fabric. Even now, a staggering number of protesters continue to die.
The government’s continuous failure to resolve the farm bill dispute, may result in one or more different scenarios, such as aggressive law enforcement actions or incidents of random and scattered violence or even a prolonged low-intensity rural armed conflict, with unimaginable human and material loss.
ALSO READ: Farmers Agitation Is Modi Govt’s Biggest Test
The protest has gradually reached a monumental juncture nationally beyond the strategic encampments at various entry points to New Delhi, with increasing global support. It is slowly starting to receive attention from the UN human rights processes. On February 11, 2021, the La Via Campesina representative spoke at a high-level special event of The UN Committee on World Food Security and said that “thousands of farmers in India are on the streets for over [the past] 75 days demanding a fair support price for their harvest. They are worried because of the entry of big agribusinesses and contract farming models that will push down their incomes further and they will have no chance to bargain.”
Michelle Bachelet, UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, in her oral updates on the global human rights situation in more than 50 countries at the 46th session opening of the UN Human Rights Council, provided much needed and belated impetus to protests when she highlighted that “continued protests by hundreds of thousands of farmers [in India] highlight the importance of ensuring laws and policies are based on meaningful consultations with those concerned. I trust that ongoing dialogue efforts by both sides will lead to an equitable solution to this crisis that respects the rights of all. Charges of sedition against journalists and activists for reporting or commenting on the protests, and attempts to curb freedom of expression on social media, are disturbing departures from essential human rights principles…”
Given the global attention the protest is receiving, it is likely that peasants and rural workers globally may observe the forthcoming International Day of Peasant’s Struggle on April 17, 2021, in support of the Indian protests. This day commemorates the massacre of the peasants and landless workers by armed forces in 1996 in Brazil while protesting for comprehensive agrarian reform.
If the government had been more transparent nationally during the drafting of the three farm bills, upheld its commitments under the UNDROP, and discharged its ethical responsibility and legal obligations to diligently implement them, it could have averted this crisis that continues to bring immense pain, suffering, and trauma to all, and that also has inflamed a toxic socio-political culture of intolerance.
The writer is a former UN human rights monitor in Yugoslavia and Rwanda