India’s GDP Has Doubled To USD 4.2 Trn Over Last Ten Years: IMF
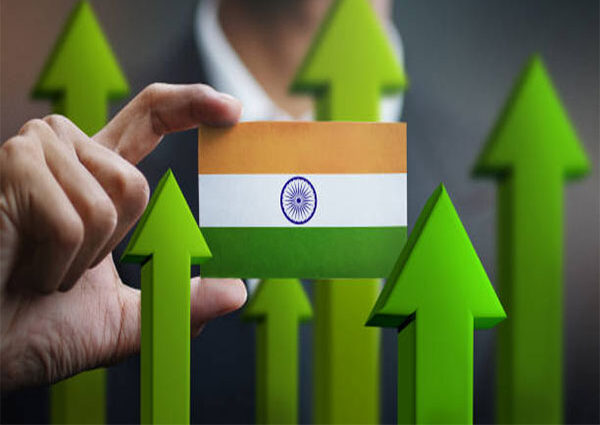
India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has doubled in size over last ten years, according to the latest data released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The data highlighted that the country’s GDP at current prices was USD 2.1 trillion in 2015 and is expected to reach USD 4.27 trillion by the end of 2025, marking a 100 per cent increase in just ten years.
The IMF also highlights that India’s real GDP growth rate for the current year stands at 6.5 per cent, indicating a strong and stable expansion of the economy. Real GDP growth refers to the increase in the value of goods and services produced in the country after adjusting for inflation. India is one of the fastest growing economies in the world
At the same time, inflation remains a crucial factor influencing economic conditions. The data stated that the inflation in the country is expected to remain at 4.1 per cent. The inflation rate is now in the central bank of the country RBI’s targeted range of 4 to 6 per cent. Inflation remains a key indicator to watch as it affects purchasing power and the cost of living.
The IMF data also highlighted that the GDP per capita, which measures the average income of a citizen based on the total economic output, is estimated at USD 11,940 (or 11.94 thousand international dollars in terms of purchasing power parity). This indicates an improvement in individual prosperity and living standards over the years.
However, the data also points out that India’s general government gross debt is currently 82.6 per cent of GDP. This means that the government’s total borrowings are quite high compared to the country’s economic output.
A high debt level could pose challenges in managing fiscal policies, but India has continued to maintain its economic momentum despite this and the government is continuously achieving the fiscal targets.
The latest IMF figures highlight India’s strong economic resilience, with a sharp rise in GDP, steady real growth, and improving income levels. However, factors like inflation and high public debt remain key areas to monitor in the coming years. (ANI)