Why Arvind Kejriwal Still Has The Edge In Delhi Polls
As Delhi goes to the polls on February 8, and campaigning by the three main political parties hots up, there is much speculation over who could win this key election. The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which runs the central government, has been recently bruised by defeats or weak performances in other state elections. It would want to regain its position by winning Delhi. But Delhi’s incumbent Aam Admi Party (AAP) government, currently in its second term, enjoys popularity and is largely not beset by anti-incumbency factors. Many believe, however, that the recent student protests in Delhi, which led to unprecedented violence across the city, particularly in university campuses, will have a bearing on the outcome of the elections.
Delhi is not a full-fledged state. Its government, no matter which party or alliance gets to form it, has limited jurisdiction over its administration. For instance, the state, home to nearly 30 million people, is policed by a force that comes under the central government’s home ministry and not the Delhi government. Likewise, matters relating to the state’s land come under the central government and not the state. The New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC), which administers the central part of Delhi, including what is known as Lutyens’ Delhi, is under central government’s authority, while the three other municipal corporations for the rest of the state are governed by elected councillors but has blurred reporting lines—they report to the central government-appointed Lieutenant-Governor but are also partly funded out of the state government’s budgets.
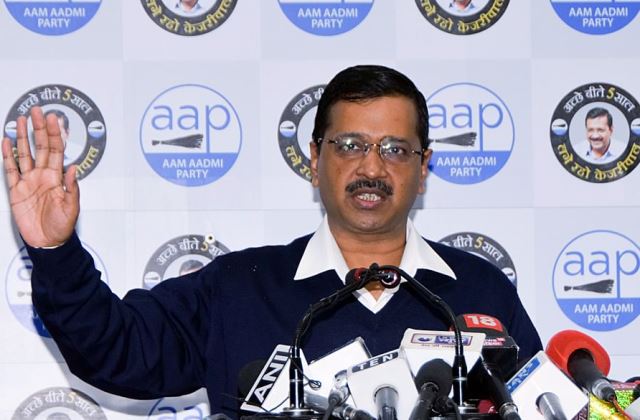
When the government at the Centre and the government of Delhi’s state are politically aligned, the system works better. However, for the past five years, Delhi’s government has been led by the Aam Admi Party (AAP), headed by chief minister Arvind Kejriwal, which has been at loggerheads with the central government and the Lieutenant-Governor. The Kejriwal government has been rooting for full statehood for Delhi as it feels, and probably rightly so, that its powers are hobbled by constraints.
During his two tenures—the first one lasted 49 days—Kejriwal has formed governments that have been remarkably transparent and largely untainted by corruption or any other scandals. His schemes, aimed at the poor and lower middle class segments of the population, have included free bus services for women, and reduced electricity and water bills, which have found great favour by ordinary voters. Besides, he has burnished his reputation as a representative of the common man by not eschewing his original activism. Kejriwal’s AAP gained popularity before he won electoral victories by staging protests to back citizens’ needs. Even as a sitting chief minister of Delhi, he has continued to build that image. He sat on a dharna in front of the Lieutenant-Governor’s office when the latter was not clearing files related to some schemes. And he continues to be the rallying point for anti-BJP voters.
It is true, however, that Kejriwal’s party turned in a poor show in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections when he failed to win a single seat in Delhi. But in following months, he has recalibrated his position. When the NDA government brought the bill to bifurcate Jammu & Kashmir and scrap Article 370, Kejriwal promptly supported them. Kejriwal’s decision to support abolition of 370 comes from the understanding that in the Lok Sabha polls, a large number of Muslim voters had voted for the Congress. So, if Kejriwal cannot depend on a section of the Muslim vote, he would rather woo the wider Hindu vote-base. It’s a political gambit based on chasing electoral numbers. Whether it will work or not depends on how the BJP woos Delhi’s voters.
While Modi’s popularity among voters remains high, the BJP’s chief ministers can’t take their popularity for granted. This is evident from the string of losses the BJP has suffered in the assembly polls during the past year. Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra have not seen continuation of the BJP government. So, at the state level, the BJP looks vulnerable. Moreover, in the forthcoming Delhi elections, the BJP has not anointed anyone as the party’s contender for the chief minister’s post. Many voters will likely see the contest in February as a “Kejriwal vs. Who?” fight. It is likely that they could opt for the sitting chief minister as their preferred choice.
In all of this, the Congress’ position is the most vulnerable. In Delhi, the Congress is disadvantaged as it has no clear face to lead its charge. Its organisational disarray at the national level can also impact its fortunes in the elections. Kejriwal, on the other hand, has been quick to grab any opportunity to create an edge for himself and his party. The questionable conduct of the Delhi Police during the current student protests—in one instance, it entered a university campus and used violence against unarmed protestors; in another, it stood as passive bystanders while hooligans entered and laid siege in another campus and unleashed violence against students.
Delhi’s urban youth voters have rallied with student protestors and their collective disposition towards the BJP government has been changing. Urban youth in India have begun viewing the BJP and its recent efforts to change the Citizenship Act as discriminatory actions that go against the fabric of secularism that the Constitution of India guarantees. In Delhi, which has been the hotbed of student protests, this is most pronounced. Willy nilly, this could work to provide further advantage to Kejriwal and his party. Delhi’s youth who form a significant proportion of the electorate could prefer AAP to the BJP or the Congress. And, along with the poor and lower middle class voters, they could steer Kejriwal to a third term in the race for Delhi.