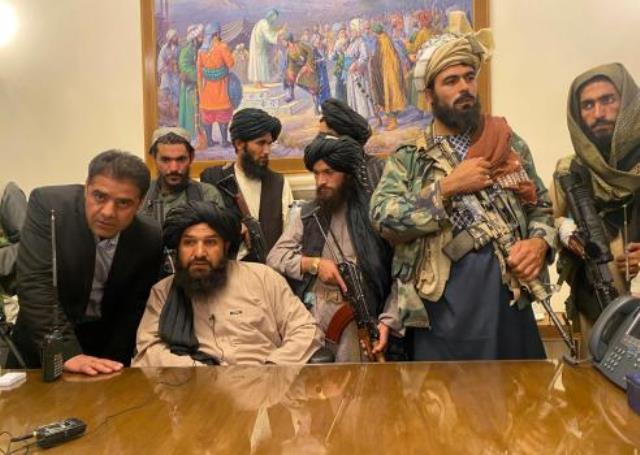
Now that the Taliban has been declared winner in Afghanistan and its elected President Ashraf Ghani fled the country on August 15, 2021 without putting up a fight, the world, especially those in the region are assessing the implications of Taliban rule. The departure of United States Armed forces has been the catalyst for the series of events and emerging geopolitical shifts that will necessitate new thinking in Indian Foreign policy.
US entered Afghanistan to eliminate the Al Qaeda network and its Taliban supporters who were responsible for the attacks on the United States soil. The leader of Al Qaeda responsible for the 9/11 attacks has been eliminated but the Al Qaeda network survives as obviously do the Taliban. The United States may still have some influence on the new Taliban, but for India the political terrain is tectonically different.
India is invested heavily in Afghanistan since the end of the Cold War. In terms of geopolitics in South Asia, Afghanistan accords a vantage point for India vis-à-vis Pakistan, it’s arch-rival. Matters are complicated further with the realization that China with its financial muscle and intention to expand the Belt and Road Initiative will find a stronghold in Afghanistan. Beijing made overtures to the Taliban leadership and met them in Qatar recently. With strong China-Pakistan relationship, India’s situation in the region becomes precarious as it may not have any leverage on its Western expanse.
India’s western borders have remained a concern historically and it expends a lot of energy and investment to consolidate and remain visible in the region. With its immediate neighbour Pakistan, not an ideal one, New Delhi looks towards Afghanistan and Iran, to both manage the western neighbourhood and to balance Pakistan.
India, therefore, has made significant investments in Iran and Afghanistan which are Pakistan’s neighbours towards west. India, imports crude oil from Iran even at the displeasure of the USA, and has invested in creating infrastructure (Schools, Hospitals and Roads) in Afghanistan. It has remained a cornerstone of India’s western geographical strategy.
The returns New Delhi may have been expecting in the form of connectivity and transport networks in the region now stand jeopardized. Under the New Silk Road Strategy of the USA, India would have gained access to Central Asia through Iran and Afghanistan. The current situation, however, alters the dynamic as the Taliban have expressed their resentment with India in the recent past and have gone to declare it as an adversary. India’s increasing proximity towards the United States may have resulted in the Taliban to dislike India.
Pakistan, on the other hand, has harboured the Taliban in safe havens on its Western tribal provinces during their difficult years and will influence decision-making in Afghanistan. Furthermore, it will work towards negating India and reducing its existing footprint in Afghanistan. As China has already approached the Taliban it is likely to extend its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) projects into Afghanistan via the China Pakistan Economic Corridor. In collaboration with regional power China, Pakistan will work to reduce India’s engagement in Afghanistan. The current geopolitical situation, therefore, is favourable for Pakistan.
India needs to take these developments into its stride and create opportunities to engage with the Taliban afresh. A positive beginning could be acceptance of the Taliban as the current interlocutors for Afghan people.
Internationally, a host of states have expressed their willingness to talk to Taliban as the ruling dispensation of Afghanistan. It may be because of the swiftness with which Taliban has occupied Afghanistan and it seems there is no challenge to Taliban and a civil war is unlikely. India also needs to engage with the Taliban for multiple reasons ranging from the investments made there to the inclusion in connectivity projects to pure geostrategic concerns. India can take heart from the fact that it evokes a lot of goodwill among the Afghan people.
Significantly enough, questions remain about the capacity of Taliban to govern a complex country. First, it will have to raise an economy from scratch to employ the younger generation of Afghanistan (60% of Afghan population is below 20 years of age). Whether China and Pakistan, two main allies of Taliban will be able to revive Afghanistan, remains to be seen. Second, current dominance of Taliban over the entire country will come under strain when local tribal warlords gather strength, aided by the West. The irony is that Taliban will still be riding the infrastructure built by the United States and its allies and India, whom they despise.
Third, acceptability for Taliban in the international system will also depend on the issue of human rights, most importantly women’s rights as they impose Shari’a law under the Islamic Republic in the territory. It is the fear of reprisals from the Taliban and the Shari’a which is causing the mass exodus of Afghans.
India, has been a favoured destination for common Afghans for generations and the international opinion is against the Taliban. India’s diplomatic efforts and negotiating capabilities to engage with the Taliban government will be crucial in the days and years to come. India must forsake idealistic notions in a realist world and should diplomatically engage with Taliban to protect its interests and to stay relevant in the region.