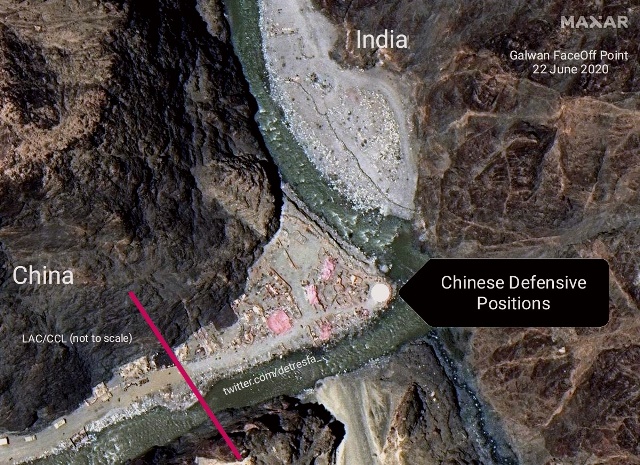
The border standoff
between India and China in Ladakh continues amidst calls from the international
community to tone down the rhetoric and resolve the issue bilaterally. India and
China, on their part have continued deliberations at both diplomatic and
military levels. The nuances of negotiations, though, not available through the
media to the general public indicate that the talks initially, were centred around
de-escalation of the situation wherein violence had occurred on the night of 15th
June in Galwan Valley and there were number of casualties on both sides.
Gradually, the discussion moved towards the process of disengagement as both
the parties had amassed a huge number of troops in the region.
The roots of the current standoff, however, go back to the months of April and May this year when the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) of China moved to the many patrolling points on the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and built structures (permanent and temporary). The build-up of the Chinese troops along the LAC which is disputed at many places and substitutes for the international border, till one is finalized, was unprecedented and reminded of the Chinese tactics of occupation in the South China Sea. Boundary-making process is a very sophisticated technical exercise which involves primarily four stages of Definition, Delimitation, Demarcation and Administration.
In the case of the
LAC, even the first stage which involves defining the boundary on the map is
not clear at many points and locations. The matter becomes more complicated
with the Chinese ignoring continual Indian demands to share the maps with the
Chinese perception of the LAC. Though the mechanisms to resolve the boundary disputes
are in place since the year 2005, the Chinese have refused to share the maps in
all the deliberations. This raises a lot of questions and problems and has been
one of the major challenges for the Indian side. The Chinese perception which
they have often invoked in the media through their spokesperson have never been
displayed through maps.
Nevertheless, even
during this difficult phase, the discussions between the two sides have
continued: at the External Affairs Minister level and at the level of the
National Security Advisors of both the countries. This is followed by the talks
by Corps Commanders of India and China at the ground situation in Ladakh.
Chinese focus, however, remains on the disengagement and de-escalation and they
have made it a very protracted process with constant insistence on the
perceptions of the LAC. It is noteworthy that progress has been made on the
ground over the course of the last month and forces have been gradually moving
back to their respective territories and away from the LAC.
Indian Analysts, on
the other hand have argued that total disengagement will be a long haul,
especially at the Pangong Tso and the Depsang Plains. These two spots are
extremely critical from India’s military and strategic perspective and that is
precisely the reason that the Chinese want to maintain a stranglehold over
them. The Depsang Plains lie in close proximity to India’s Air Force Base at
Daulat Beg Oldie which is advantageous to India in adverse conditions.
At the Pangong Tso,
the LAC is disputed and according to reports, Chinese have encroached more than
8 kms. inside the Indian version of the LAC which runs at Finger 8 (fingers are
mountain features jutting out into the lake from the North Bank) and the Indian
Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) used to patrol till this point. The Chinese have
occupied area till Finger 4 and have built concrete structures effectively
covering more than 60 square kms. of the area and therefore will be difficult
to evacuate through negotiations. On the other hand, one of the parties can
afford a conflict.
Indian stance,
therefore, should be to press the negotiations towards the restoration of the status
quo ante, or the situation which existed prior to the month of May 2020. Media
reports in India indicate that during the last round of talks between the Corps
Commanders on 14th-15th July, demand for status quo
ante has been made by the Indian side to Chinese counterparts. Chinese
media reports indicate little and only say that progress has been made on the
disengagement of forces.
On the other hand, the
pattern along this part of the LAC, due to altitude, difficult terrain and
inclement weather conditions is that of withdrawal of forces from heights
during the winter months and moving back to the permanent bases in the area. Given
the situation this year this may not happen at Pangong Tso and Depsang Plains
and the Indian side should be ready to face the vagaries of weather, terrain
and altitude.
The experience of the Indian
Army at the Siachen Glacier can be drawn to withstand the Chinese in the area.
One way or the other, the strategic geography of the area of these crucial
points will play an important role in the future of this picturesque
militarized space.