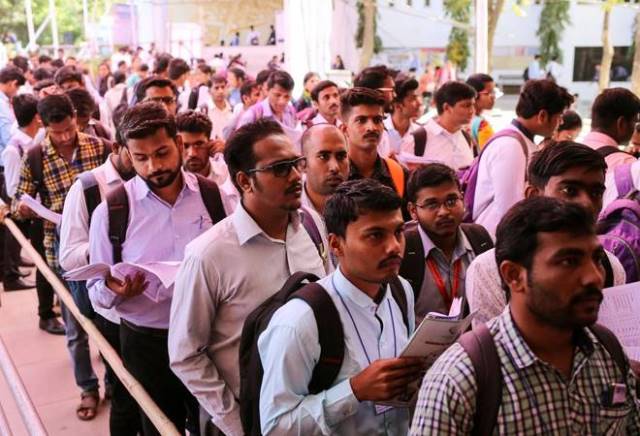
What are the major concerns of Indians today? According to the December issue of Ipsos, the global market research and public opinion specialist, the three burning headaches of urban Indians are unemployment (41%), financial and political corruption (29%) and coronavirus (29%). These are followed by urban Indian worries about crime and violence (25%) and poverty and social inequality (25%). India is one of the 26 countries that feature in Ispos periodic review of citizens’ perception as to whether the things are moving in the “right direction” or “are they off on the wrong track?”
One can always make an issue of the quality and breadth of the survey sample size and how good are interviewers in engaging interviewees in discussions. Whatever that may be, this work of Ispos has won global recognition and there should be no hesitation in accepting that urban unemployment is hitting growing numbers of people across the country as the third Covid-19 wave in the form of mutant Omicron spreads fast. The curse of people going without work and therefore, drying up of their income is being increasingly manifest in rural areas too.
The job data report by the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) saying unemployment rate in the country touched a four-month high of 7.91% in December comes as confirmation of popular concern of lack of employment opportunities. It will be poor consolation to say that the country had experienced an unemployment rate of 8.3% in August.
According to CMIE, the urban unemployment rate in December rose to 9.30% from 8.21% in the previous month. In rural areas, unemployment rate during the period was up from 6.44% to 7.28%. Remember people living in rural areas constitute close to 70% of the country’s population. This should give an idea of hardships of rural people without ownership of land. CMIE report says new jobs were created in December, but these were far less than people joining the ranks of jobseekers.
“Around 8.3 million additional people were looking for jobs. However, 4 million jobseekers got employment,” says CMIE managing director & CEO Mahesh Vyas. What is happening on the employment front is not surprising against the background of muted economic activity and consumer sentiment downed by Omicron. From an ill-advised demonetisation that badly hit the informal sector and a fairly large part of building construction activities across the country to clumsy rollout of GST, a number of policies were found to be anti-job growth.
State Bank of India says in a recent report that progress of formalisation of the economy has seen the share of informal sector in GDP falling from 52% in 2017-18 to 15-20% in 2020-21.The report has found that ₹130 million crore has come under the formal economy in the last few years. Formalisation is to be welcomed, for it brings increases in output and turnover by firms, which are liable to pay taxes. Cash intensity of the economy will continue to diminish as the government continues to give thrust to cashless transactions, promote digital payments and kisan credit cards and transfer of all kinds of cash benefits to beneficiary bank accounts.
ALSO READ: Covid Has Deepened India’s Poverty Pit
While all that is good for the economy, the question remains as to what extent job losses in the informal sector have been made good by creation of new jobs in the formal sector. Precise figures are not available. But one can easily guess the privation of people who became redundant in the process of emasculation of informal sector gaining pace since the breakout of Covid-19. No wonder more and more faces of jobless Indians stand frazzled.
The unemployment situation being so critical, New Delhi is pushing profit-making public sector undertakings to take up major capital expenditure programme along with green signalling construction of new highways and other infrastructure projects. At the same time, the banks are encouraged to fund private sector greenfield projects and also its expansion at present operating sites. Infra work is always employment intensive, though not of permanent kind. At the same time, because of high levels of automation and digitisation, investments in manufacturing industries are now generating lesser number of jobs than before.
Let’s consider the ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel (AMNS) announcement to build a massive 24 million tonne (mt) steel plant in Kendrapara district of Orissa (since renamed Odisha) at an investment of over ₹10 million crore. The joint venture company will run the plant permanently employing only 16,000 people. No doubt, the proposed steel plant will create significant indirect employment opportunities several times bigger than direct employment in the mother plant through ancillary and downstream industries and services. But compare the direct employment to be created by AMNS investment at Kendrapara with Tata Steel’s 31,189 people on roll (2020-21 annual report figure). The more than a century old Tata Steel has capacity of 19.6 mt at its three mills at Jamshedpur and Odisha.
Odisha chief minister Naveen Patnaik is aware that the state’s rich endowments of mineral resources, including iron ore, coal, chromite manganese ore and bauxite must not only be used to make primary metals such as steel and aluminium but these must be further value added within the state to generate employment for the local people and revenue for his government. That is why at the prodding of Patnaik, the National Aluminium Company and Vedanta Aluminium are building aluminium parks adjacent to their smelters where small and medium units will get liquid metal to make value added aluminium products.
Vedanta Aluminium CEO Rahul Sharma says his company promoted aluminium park will bring in “investment of at least ₹2,000 crore, create an annual incremental economic value of ₹4,500 crore for the state and generate livelihood for more than 10,000 people.” Steel mills and aluminium refineries and smelters in Odisha are found in areas where tribal population is in majority. Ancillaries linked to mother plants and downstream units for value addition to primary metals create many jobs but they need skilled hands. Here the state – in this case Odisha – will have to build institutions in concerned districts to impart skills to tribal and people belonging to Scheduled Castes and Tribes to be ready to work in factories.
India’s rapidly expanding information technology sector, fintech, which is inviting considerable support from venture capitalists and start-ups mounted on IT are the exceptions where supply of human resources are to fall short of growing requirements for at least the next five years. The country’s largest staffing solutions provider Teamlease says fulltime employee attrition in the technology industry will rise to 22% by March 2022 when attrition in contract staffing will be 49%. Shortages of IT and engineering human resources leading to high rates of job hopping are a global phenomenon that is not going to go away any day soon. At the same time, the problem is manifest more in India and other sourcing countries than destination places such as the US and Europe. In their desperation to retain talents, many Indian employers in IT and e-commerce industries are increasingly resorting to the practice of making better offers to people who have served notice to quit. The practice, however, in many cases is proving counterproductive. With counteroffers in hand, the ones having decided to leave in any case get a handle to strike a better deal with new employers.
The counteroffers could result in demoralisation of performers who are not looking for greener pastures. The competitive bidding game is a no-win practice. Shortages of human resources in the specialised niche sectors call for colleges, universities and IITs to raise capacity to produce larger number of IT experts. At the same time, the IT groups and manufacturing companies digitising their operations will have to have bigger budgets for employee up-skilling.