People listen to weather reports to plan their days or weeks for chores
such as when to put out clothes to dry, go out etc. Perhaps the weather man never
thought that weather reports can be weaponized. It is India which lobbed the
first weather report bomb starting the weather report wars with Pakistan.
The strategy thought out in the secret meeting rooms of the Indian
strategic defence cabals is to make a virtual claim on Pakistan Occupied
Kashmir as called in India, or Azad Kashmir as named by Pakistan. ‘Doordarshan’
is under instruction to pretend that POK is Indian. It is to give the daily weather
reports for all of Kashmir including POK but call it simply Kashmir.
Not to be outwitted, Pakistan retaliated with the same. They are now
giving weather reports for all of Kashmir, including Jammu and Ladakh, as if they
were all part of Pakistan. It is all about visual representation of territory.
Visual representations of territory have played a
significant role in the national imagination of people. Nations and states have
reinforced such representations through school textbooks, maps, documents,
decrees and legal instruments. In the age of mass media, internet and related
proliferation of information, any news can become a source of confrontation
between states.
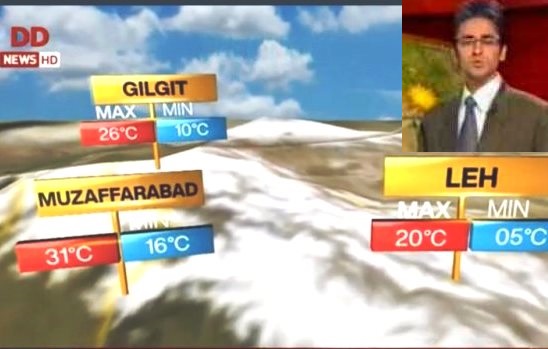
The Indian official television broadcaster,
Doordarshan, has adopted a new media offensive now for over a week. Weather
bulletins on Doordarshan and All India Radio have started featuring weather
forecasts of Mirpur, Muzaffarabad and Gilgit-Baltistan area of Kashmir over
which Pakistan has territorial control and India claims the territory. In a
reaction to this, Pakistan has carried weather reports of the Indian side of
Kashmir on its official television channels.
Notably, Indian broadcasts follow the bifurcation of
the state of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) into two Union Territories (Jammu and
Kashmir and Ladakh) under the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019 in August
2019. In the same month, India had
already revoked Article 370 of Indian Constitution which accorded special
status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir, and involved special provisions for
the residents of J&K. Pakistan at that point had raised the issue at the
United Nations without much success. India is now unravelling its grand design
and making people imagine POK as if it is part of India.
Geopolitically, this is a well-known strategy of
claiming territory with the approach of place-naming and place-making and
establishing a norm through repeated usage of suitable nomenclature that the
place belongs to us. Examples abound of creation of a sense of belonging by
such means by India’s erstwhile colonizers, the British. Historically the
British were an important factor in the current territorial dispute at India’s
northern expanse as to who the territory belongs to.
An important task of the state is to invoke a
territorial image of the state and familiarize the larger population with it. School
textbooks and official maps play this role effectively to make its territory
and places legible for the state population. Place-making often involves
creation of new activities, economic or otherwise at a particular location. In
this case, the weather forecasts is one such activity, with which not only the
Indian State but the people can also identify.
As critical geographical as it may sound today to
investigate the British colonialist and imperial exercises, it is instructive
that such methods of place-naming and place-making have existed even in ancient
Indian texts like Puranas, the Epics and related texts. The geographical
references to seven dwipas, including Jambu Dwipa cover the whole
Eurasian expanse in detail with Mount Meru (The Pamir) as the centre of
the Eurasian continent. The description stretches to as far as the
Mediterranean and the Eastern coast of Africa.
Furthermore, there is astonishing detail about the
orientation of the Himalayas and the adjacent mountain ranges. The river
systems originating from the present-day Tibet are explained in detail with the
directions of the flow of rivers. The “Puranas” include, the origin of the
universe and the earth, the oceans and continents, mountain systems of the
world, regions and their people and astronomical geography” (Ali, 1966). However
such detailed descriptions were never laden with the ideas of capture or
control of territory but only for the sake of geographical knowledge.
Within this literature, the expanse of Bharatvarsa
is mentioned in detail on numerous occasions. This fact of geographical unity
of the subcontinent remained unchanged and unchallenged until the moment of
partition in 1947. The partition in 1947 essentially created a rupture in the
regional, human and physical geography of the Indian sub-continent into two
separate states of India and Pakistan. Perhaps, it is this longer geo-historical
imagination that takes precedence over recent history since partition when the
weather reports are broadcast on the national television channels.
The territorial claims in Kashmir are now becoming
more visible and perhaps a beginning of a new geopolitical imagination of post
1947 India is being given shape and root.
Since 2014, the Indian government’s approach under the
leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been quite assertive on the issue
of Kashmir and related terrorism emanating from Pakistan. The response to acts
of terrorism has been more in terms of military action at the Line of Control,
But for the first time a nuanced approach to visually construct that represents
the whole Kashmir as Indian, has been adopted.
Reports indicate that Mr. Ajit Doval, the National
Security Advisor who is also an intelligence expert on Pakistan, has been
instrumental in developing and implementing this strategy of weather
forecasting of the larger territory of Kashmir and thereby indicating that it
is Indian. On the other hand, reactions of the international community may only
become evident when real world diplomacy resumes after the end of the global
shutdown due to the CoVID19 pandemic. Until then, the otherwise innocuous weather
report, produced by non-political meteorologists, has become the new political battle
ground between India and Pakistan.
Dr Krishnendra Meena is Assistant Professor
and teaches at School of International studies, Jawaharlal Nehru University,
New Delhi