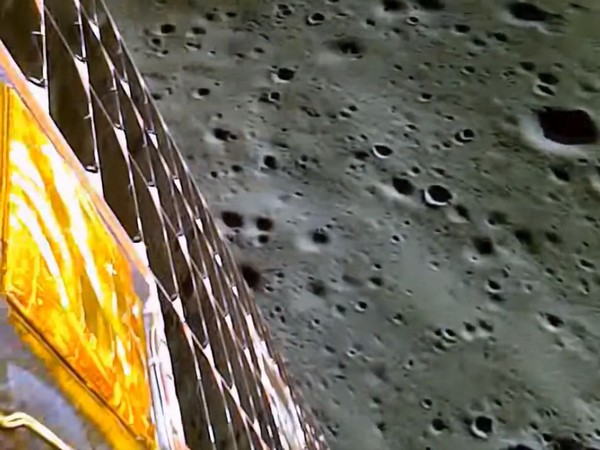
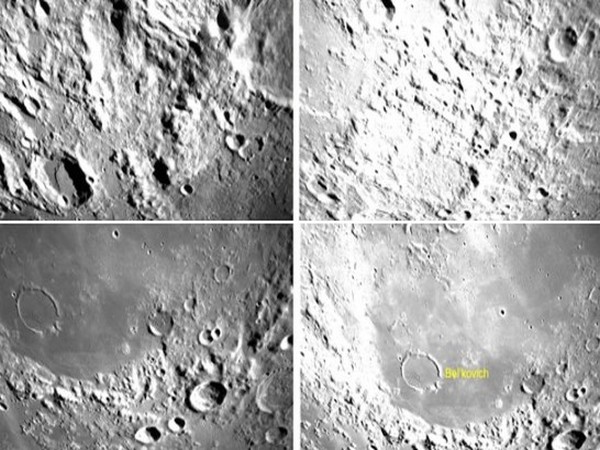
Aditya-L1 spacecraft, India’s first solar mission, that is destined for the Sun-Earth L1 point has taken images of the earth and the moon.
India’s space agency- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the selfie and images taken by the Aditya-L1 that has successfully performed the second earth-bound manoeuvre on Tuesday.
Sharing a video on social media platform on ‘X’, the ISRO said, “”The earth and the moon as seen by the camera on-board Aditya-L1 on September 4.”
The ISRO, on September 2 launched the country’s maiden solar mission — Aditya-L1 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota on Saturday.
It carried seven different payloads to have a detailed study of the sun, four of which will observe the light from the sun and the other three will measure in-situ parameters of the plasma and magnetic fields.
Aditya-L1 will be placed in a halo orbit around Lagrangian Point 1 (or L1), which is 1.5 million km away from the Earth in the direction of the sun. It is expected to cover the distance in four months’ time.Aditya-L1 will stay approximately 1.5 million km away from Earth, directed towards the Sun, which is about 1 per cent of the Earth-Sun distance. The Sun is a giant sphere of gas and Aditya-L1 would study the outer atmosphere of the Sun.
ISRO said Aditya-L1 will neither land on the sun nor approach the sun any closer.
This strategic location will enable Aditya-L1 to continuously observe the sun without being hindered by eclipses or occultation, allowing scientists to study solar activities and their impact on space weather in real time. Also, the spacecraft’s data will help identify the sequence of processes that lead to solar eruptive events and contribute to a deeper understanding of space weather drivers.
Major objectives of India’s solar mission include the study of the physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism, the solar wind acceleration, coupling and dynamics of the solar atmosphere, solar wind distribution and temperature anisotropy, and origin of Coronal Mass Ejections (CME) and flares and near-earth space weather.
Aditya-L1 is a satellite dedicated to the comprehensive study of the sun, which will find out the unknown facts about the sun. The satellite will travel on Earth-bound orbits for 16 days, during which it will undergo five manoeuvres to gain the required speed to reach its destination.
Subsequently, Adiya-L1 will undergo a trans-Lagrangian1 insertion manoeuvre that will take 110 days. The satellite will travel approximately 15 million kilometres to reach the L1 point. Upon arrival at the L1 point, another manoeuvre binds Aditya-L1 to an orbit around L1, a balanced gravitational location between the Earth and the Sun, according to information shared on ISRO’s official website. (ANI)
Read More: https://lokmarg.com/